Total Knee Replacement – TKR
Total Knee replacement is a surgical procedure that replaces injured or worn-out parts of knee joints. TKR is a permanent solution, resulting in painless knee joints while walking, sitting or lying down.
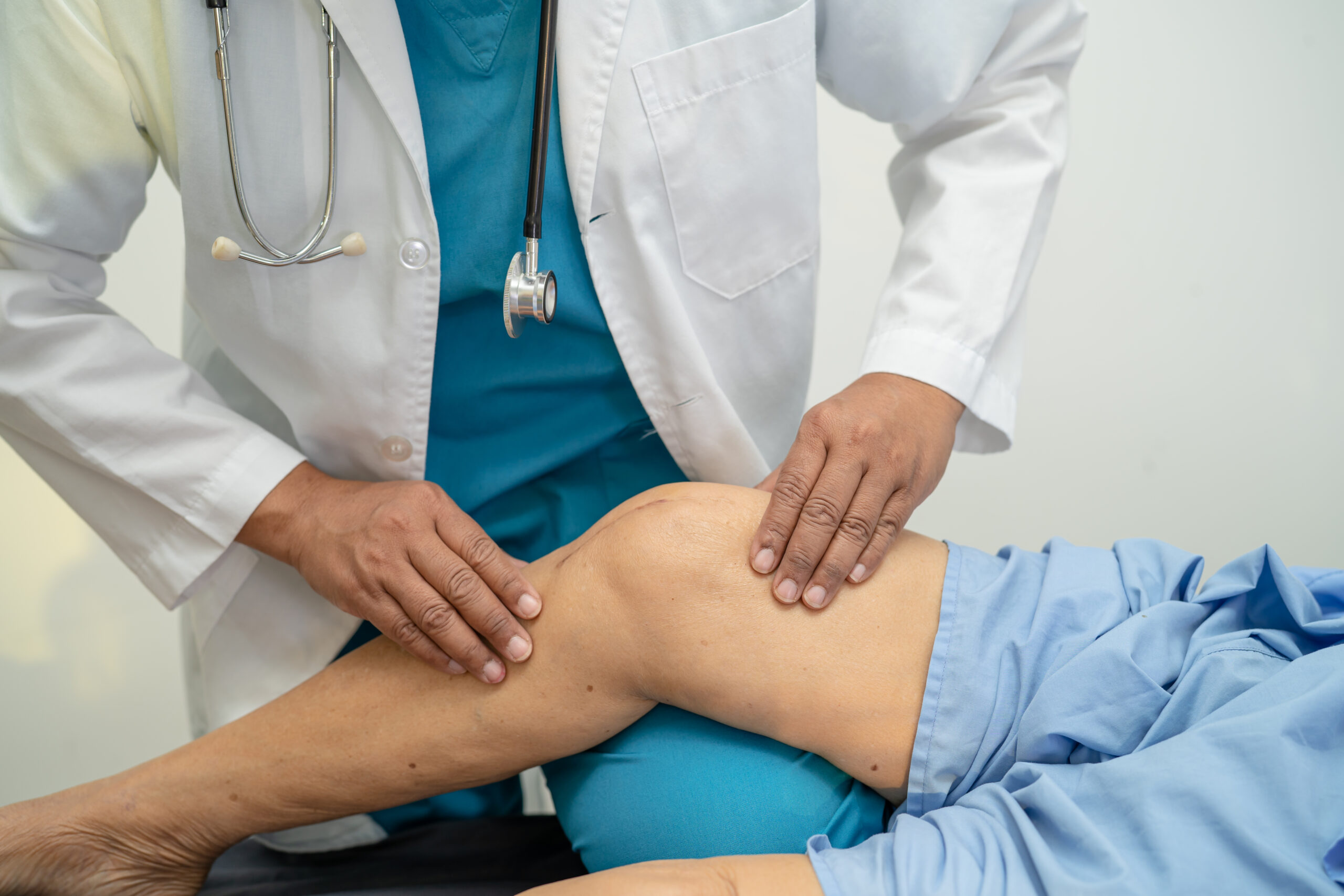
Types of Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
All cartilage is removed from the knee joint and replaced with metal and plastic prosthetics.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR)
Also called Unicompartmental Arthroplasty (UKA), it is a minimally invasive surgery wherein only the damaged compartment is replaced with metal and plastic.
Knee-cap Replacement
Also called a Patellofemoral Replacement, this involves replacing just the affected under-surface of the kneecap and its groove (the trochlea).
Simultaneous Bilateral Knee Replacement
Both knees are replaced at the same time. This procedure lowers the infection rate associated with a single surgical event.
Revision Knee Replacement
These are Total Knee Replacements that need to be revised after 15-20 years (post-primary surgery). It is performed via highly-advanced prosthesis and Computer Assisted Surgery (CAS).
Signs & Symptoms of Total Knee Replacement (TKR) Need
- Severe knee pain
- Stiffness in knees that limits routine activities like walking and sitting
- Posttraumatic degenerative joint disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis/Inflammatory arthritis
- Osteonecrosis/joint collapse with cartilage destruction
Treatment of Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Step 1
The patient is given general anesthesia. At times, it is replaced with either spinal or epidural anesthesia and a nerve block.
Step 2
The surgeon makes an incision of 8-12 inches to expose the knee joint. The damaged bone is removed along with the cartilage on the end of the femur and tibia from the bone surface. The surrounding muscles, ligaments, and the knee cap are preserved.
Step 3
The surfaces that hold the metal and plastic components are shaped.
Step 4
The artificial material is implanted over both bones. The metal cap is implanted on the femur surface and the plastic part is implanted on the tibia surface using cement or screws. These together form the joint for support and function as a new knee joint.
Step 5
The cut is closed with stitches and covered with dressing.
Other Treatments
- Arthroscopy Knee Surgery
- Bariatric/Laproscopic
- Bone Marrow Transplant
- Elbow Surgery
- Gastroentrology & Liver Transplant
- General Surgeon
- Heart Transplant
- IVF
- Kidney Transplant
- Laproscopic and Minimal Access Surgery
- Laproscopic, Minimal Acess, Bariatric
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Orthopedics
- Shoulder Replacement
- Total Hip Replacement – THR
- Urology and Renal Transplant

Send Enquiry to know in More Detail
Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptat.
Learn More